10. Coding the Solution
Coding the Solution
Time to code the final solution!
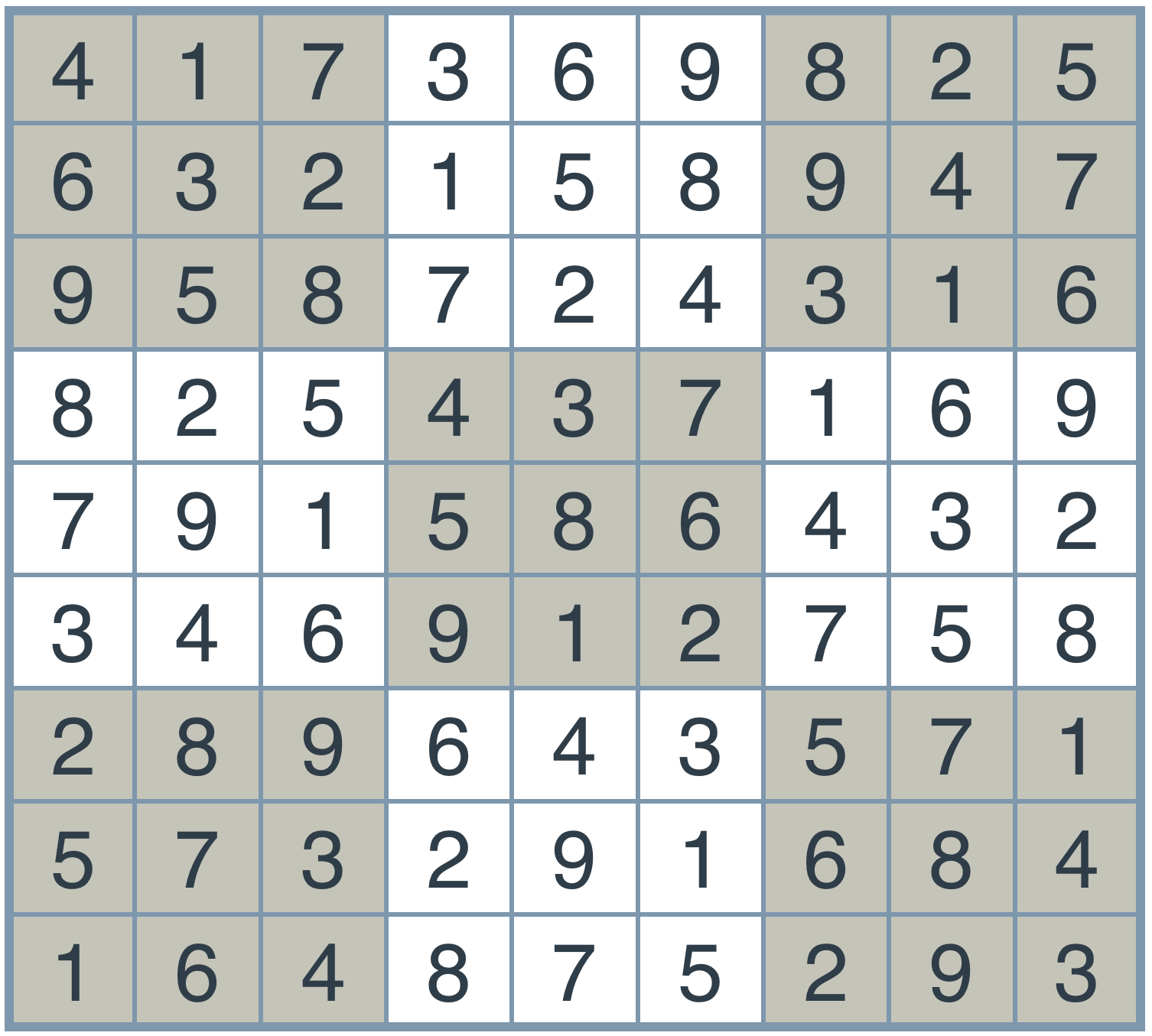
Finish the code in the function search, which will create a tree of possibilities and traverse it using DFS until it finds a solution for the sudoku puzzle.
Start Quiz:
User's Answer:
(Note: The answer done by the user is not guaranteed to be correct)
So, that seemed to do it! You should have got the following solution.